M-1
EXPERIMENT M: SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC
DETERMINATION OF IRON
OBJECTIVE
In this experiment, the principles of absorption of electromagnetic radiation by matter will be
examined. In addition, the concentration of an iron analyte in a water sample will be determined
by using a procedure called colorimetry
- an analytical method that is based upon the absorption
of visible light by colored compounds in solution.
THEORETICAL CONSIDERATIONS
In spectroscopic methods of analysis, a sample is irradiated with a coherent beam of
electromagnetic radiation from an appropriate source. A portion of the radiation is reflected,
some is absorbed and the remainder is transmitted. The amount of radiation absorbed by a
species in a solution is related to the concentration of that species in solution. Visible
spectroscopy, also known as colorimetry, is the most widely used method of analysis in the
laboratory. Most substances can be converted to colored derivatives and, hence, their
concentrations determined by visible spectrometry.
A.
Properties of Light
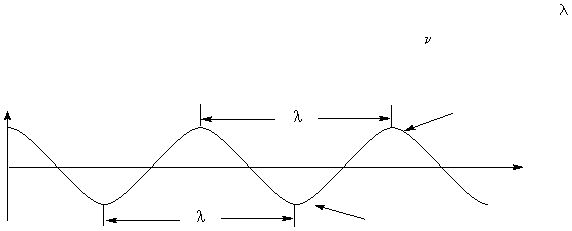
Electromagnetic radiation can be considered to be a form of radiant energy that is propagated
through space as a wave. It vibrates perpendicular to the direction of motion and this imparts a
wave motion to the radiation. The wave can be described either in terms of its wavelength (
),
the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs, or its frequency (
), which is the number
of crests or troughs that pass a fixed point per unit time.
Trough
Crest