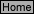
M-2
The reciprocal of the wavelength, the wavenumber, is the number of waves present in one
centimeter. The relationship between frequency and wavelength is:
=
c
where c is the speed of light which is equal to 2.998 x 10
8
m•s
-1
in a vacuum.
In the early part of this century, Albert Einstein demonstrated that radiation is emitted not as a
continuous wave, but rather in tiny bundles or packets called photons. The energy carried by a
single photon is proportional to the frequency of the radiation,
, as expressed in Planck’s Law:
E = h
where h is Planck’s constant (~ 6.626 x 10
-34
J•s). By combining the two expressions, we can
relate the energy of a photon to its wavelength (wave-particle duality):
E = h
and
=
c
therefore:
E =
hc
From this relationship, we see that energy is inversely proportional to wavelength and directly
proportional to frequency.
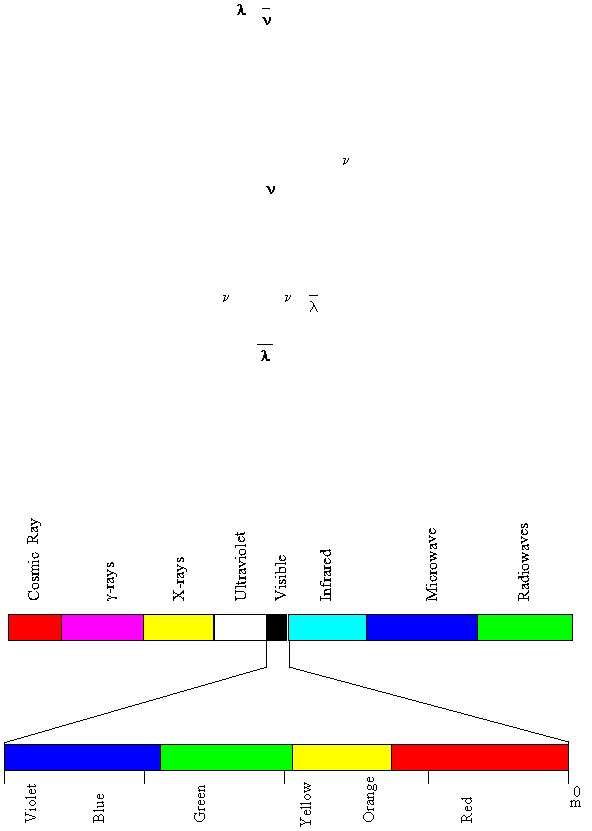
The major regions of the electromagnetic spectrum are represented in the diagram below:
400
500
600
700
80
n
m
n
m
n
m
n
m
n