I-3
amounts of HA and A
-
present in the solution. If one of these species has been completely reacted
through the addition of OH
-
or H3O
+
, then the capacity of the buffer has been exceeded and a dramatic
pH change will be observed. The maximum buffering capacity of a buffer occurs, when the
concentration of the weak acid equals the concentration of the conjugate base. On a titration curve this
corresponds to the point where pH = pK
a
(i.e. the half equivalence volume).
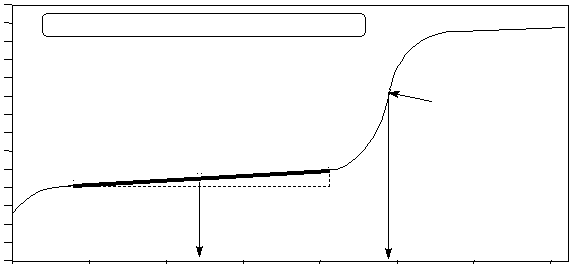
The action of a buffer solution is visible in the titration curve of a weak acid and a strong base. In
Figure 2 in Experiment H, the pH changes only by about 1.5 units between the addition of 5 and 20 mL
of 0.50 M base. In this region, the solution in the titration flask is a buffer solution.
EXPERIMENTAL METHOD
An acetic acid-sodium-acetate buffer system will be prepared by combining equal molar quantities,
resulting in a solution with the maximum buffering capacity. Samples of this solution will be used to
determine the effects of dilution and the addition of a strong acid and a strong base on the buffer
system. The effect of these additions will be monitored by observing any changes in the pH of the
solution.
1/2 Eq. vol.
Eq. vol. = 25.0 mL
Eq. Pt.
Titration of HA using 0.50 M NaOH
Volume of NaOH added (mL)
30
20
10
0
pH
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
BUFFER REGION
small
change
in pH