raising
the temperature
adding a catalyst
increasing the
concentration of reactants
increasing the
surface area of a solid reactant
increasing the
volume of the container for a gaseous reaction.
R =
k[A][B]
R = k[A]2[B]
R =
k[A][B]2
R = k[B]
R =
k[A]2
1.0 x
10-6
4.0 x 10-7
1.5 x 10-2
1.8 x
10-5
1.2 x 10-3
Heat given
off by the system increases the thermal motion of the surroundings.
The
system is going to a more ordered state.
The system is going
to a more random state.
Heat absorbed by the system increases the thermal
motion of the surroundings.
Heat given off by the system decreases the thermal
motion of the surroundings.
R =
k[A]2
R = k[A][B][C]
R = k[A]2[B]3[C]
R =
k[B]3[C]
Insufficient information to fix rate
equation
156![]() 76
76![]() 312
312![]() 12.5
12.5![]() 89.6
89.6
| Initial Concentrations, M | Initial Rate, M/s | ||
| [A] | [B] | [C] | D[D]/Dt |
| 1.0 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 1.8 x 10-4 |
| 1.0 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 1.8 x 10-4 |
| 1.0 | 0.30 | 0.80 | 9.0 x 10-5 |
| 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 1.8 x 10-5 |
R =
k[A]2[B][C]2
R =
k[A][B]2[C]
R =s k[A][C]
R =
k[A][C]-1
R = k[B][C]2
10100
1680
19500
2.15 x
10-4
7020
3.36
28.8
1.37 x 109
21.04
10.4
-4.42![]() -36.7
-36.7![]() +36.7
+36.7![]() +4.42
+4.42![]() -36200
-36200
lowering
the energy of the reactants.
lowering the energy
of the products.
providing a reaction path with a lower activation
energy
increasing the equilibrium constant.
decreasing the rate
of the reverse reaction.
Rate =
k[NO]2[H2]2/[N2][H2O]2
Rate =
k[NO][H2]2
Rate =
k[NO]2[H2]2
Rate =
k[NO]2[H2]
Rate =
k[N2][H2O]2/[NO]2[H2]2
At 700 K the rate constant is 19.7 M-1s-1. The energy of activation for this reaction is _____ kJ/mole.
362![]() 3.6
3.6![]() 114
114![]() 1.1
1.1![]() 47
47
At 680° C the rate constant for this reaction is 0.0198 s-1. How long will it take for an initial concentration of 0.57 M to fall to 0.013 M?
75 s![]() 191 s
191 s![]() 390
s
390
s![]() 28 s
28 s![]() 0.011
s
0.011
s
55 s![]() 35 s
35 s![]() 0.029
s
0.029
s![]() 0.014 s
0.014 s![]() 0.0056 s
0.0056 s
longer
shorter
the same
Not
enough information given. Must know DH to answer this.
Not enough
information given. Must know Ea to answer this.
BrO3- (aq) + 5Br- (aq) + 6H+ (aq) ® 3Br2 (aq) + 3H2O
was studied and the following information was obtained:
[BrO3-]0 |
[Br-]0 |
[H+]0 |
Initial Rate{M/sec} |
| 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 8.0 x 10-4 |
| 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 3.2 x 10-3 |
| 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 1.6 x 10-3 |
| 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 3.2 x 10-3 |
Rate =
k[BrO3-][Br-]5[H+]2
Rate =
k[BrO3-][Br-]5[H+]6
Rate =
k[BrO3-]2[Br-][H+]2
Rate =
k[BrO3-][Br-]2[H+]
Rate =
k[BrO3-][Br-][H+]2
Questions 18 through 21 are based upon the
following mechanism proposed for the
decomposition of hydrogen peroxide using potassium
bromide.
- A.
H2O2 (aq) + Br- (aq) ® H2O (aq) + OBr- (aq)
......Slow
B. H2O2 (aq) + OBr- (aq) ® H2O (aq) + Br- (aq) + O2 (g) ...... Fast
H2O2 (aq) + OBr- (aq) ® H2O (aq) +
Br- (aq) + O2 (g)
H2O2 (aq) + Br- (aq) ® H2O (aq) +
OBr- (aq)
2H2O2 (aq) + Br-
(aq) ® 2H2O (aq)
+ OBr- (aq) + O2 (g)
2H2O2 (aq) ® 2H2O (aq) + O2 (g)
2H2O2 (aq) + Br- (aq) ® 2H2O (aq) +
Br- (aq) + O2 (g
Rate =
k[H2O2][OBr-]
Rate =
k[H2O2]2
Rate =
k[H2O2]2[Br-]
Rate =
k[H2O2][Br-]
Rate =
k[H2O2][OBr-]2
H2O
Br-
OBr-
None are
reaction intermediates
Both (B) and (C) are reaction
intermediates.
H2O
Br-
OBr-
None are
catalysts.
Both Br- and OBr- are catalysts.
2.86
0.999
0.350
1.05 x
10-3
1.05
the
equilibrium constant increases.
the activation
energy increases.
the activation energy decreases.
the rate constant
increases.
the rate constant decreases.
increasing the temperature.
decreasing the
temperature.
increasing the activation energy.
decreasing the
activation energy.
decreasing DH.
0.125![]() 0.140
0.140![]() 0.250
0.250![]() 0.425
0.425
| [ICl]0 | [H2]0 | Initial Rate(Ms-1) |
| 0.250 | 0.500 | 2.04x 10-2 |
| 0.500 | 0.500 | 4.08x 10-2 |
| 0.125 | 0.125 | 2.55 x 10-3 |
| 0.125 | 0.250 | 5.09 x 10-3 |
R =
k[ICl]2
R = k[H2]2
R =
k[ICl][H2]2
R =
k[ICl][H2]
R = k[ICl]2[H2]
Use the following data for the gas phase
decomposition of
hydrogen iodide to
answer questions 27 through 29.
| t, hours | 0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 6.0 |
| [HI], M | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.25 |
![]()
one
half![]() minus one
minus one![]() zero
zero![]() first
first![]() second
second
0.25
h-1
0.25 Mh-1
0.50 h-1
0.50
M-1h-1
2.0 M-1h-1
0.25![]() 0.35
0.35![]() 0.50
0.50![]() 2.0
2.0![]() 4.0
4.0
Use the following information to answer questions 30 through 33
Hydrogen peroxide in basic solution oxidizes iodide
ion to iodine.
The proposed mechanism
for the reaction is:
- step 1.... H2O2 +
I- ® HOI + OH-
......slow
step 2.... HOI + I- ® I2 + OH- ......fast :
2I-®
I2
H2O2 + I- ® HOI + OH-
HOI + I-
® I2 +
OH-
H2O2® 2OH-
H2O2 + 2I- ® I2 + 2OH-
I-
HOI
OH-
I2
there is none
I-
HOI
OH-
I2
there is none
R =
k[H2O2][I-]2
R =
k[H2O2][I-]
R =
k[HOI][I-]
R = k[I-]2
R =
k[I2][OH-]2
0.025![]() 0.125
0.125![]() 0.50
0.50![]() 0.050
0.050![]() 0.20
0.20
Question 35 is based on the following information.
The following initial rates of the reaction were
measured at various initial concentrations as
recorded in the table below for:
CH3COCH3 + Br2®
CH3COCH2Br + H+ +
Br-
Experiment |
[CH3COCH3]0 |
[Br2]0 |
[H+]0 |
Initial Rate
(M s-1) |
| 1. | 0.30 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 5.7 x 10-5 |
| 2. | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.050 | 5.7 x 10-5 |
| 3. | 0.30 | 0.050 | 0.10 | 1.2 x 10-4 |
| 4. | 0.40 | 0.050 | 0.20 | 3.1 x 10-4 |
| 5. | 0.40 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 7.6 x 10-5 |
![]()
R =
k[CH3COCH3][Br2]
R =
k[CH3COCH3][H+]
R =
k[CH3COCH3][Br2]2
R =
k[CH3COCH3]2[Br2]2[H+]
R =
[CH3COCH3][H+]2
Questions 36 and 37 are based on the following information.
For a first order reaction the following data are
obtained from experiment by measuring
the concentration of N2O5 as a
function of time, at constant temperature.
The reaction is:
N2O5 (soln) ®
2NO2 (soln) + 1/2O2
(g)
| time (seconds) | 0 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | |
| [N2O5] | 0.100 | 0.0707 | 0.0500 | 0.0250 | 0.0125 | 0.00625 | |
![]()
6.93 x
10-3
0.0707
0.0500
0.600
200
[N2O5] V time (in sec.)
1/[N2O5] V time (in sec.)
ln[N2O5] V time (in sec.)
ln[N2O5] V 1/T(K)
average rate V
[N2O5]2
Question 38 is based on the following.
The rate constant, k for the decomposition of
acetaldehyde
CH3CHO
(g) ® CH4 (g)+ CO
(g)
is measured at six
different temperatures. The natural logarithm of k is plotted on the
vertical axis (y-axis) and the reciprocal of the absolute temperature
(1/T) is plotted on the horizontal axis (x-axis). The result is a linear
plot with a slope equal to -2.20 x 104 K and a y-intercept
equal to 27.0.
![]()
8.314
183
27.0
298
22.4
1.20 x
10-4
674
5760
330
2880
Questions 40 and 41 are based on the following graph which represents experimental data obtained from a reaction of the type
A ® products.
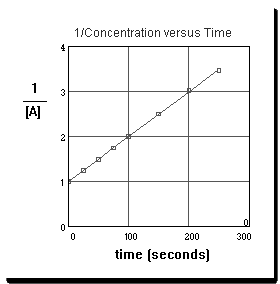
first![]() second
second![]() zero
zero![]() 1/2
1/2![]() -1
-1
100![]() 20
20![]() 0.010
0.010![]() 0.020
0.020![]() 1.00
1.00
Questions 42 through 45 are based on the following mechanism for the destruction of ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere.
- step 1..... O3(g) +
NO(g) ® NO2(g) +
O2(g) ......Slow
step 2...... NO2(g) + O(g) ® NO(g) + O2(g) ......Fast
O3(g) + NO(g) ® NO2(g) + O2(g)
NO2(g) + O(g) ® NO(g) + O2(g)
O3(g) +
O2(g) ®
O5(g)
O3(g) + O(g) ® 2O2(g)
2O2(g)
® O3(g) +
O(g)
O3
NO
NO2
O2
O
O3
NO
NO2
O2
O
larger
than that of the uncatalyzed reaction
smaller than that
of the uncatalyzed reaction
the same as that of
the uncatalyzed reaction
impossible to determine
Question 46 is based on the following information.
Chlorine Dioxide is a reddish-yellow gas that is
soluble in water.
In basic solution
it reacts according to the following equation:
2ClO2 (aq) + 2OH- (aq) ® ClO3- (aq) +
ClO2- (aq) + H2O
The following initial rates of the reaction were measured at
various initial concentrations
as
recorded in the table below.
| Experiment | [ClO2]0 | [OH- ]0 | Initial Rate (M s-1) | |
| 1 | 0.060 | 0.030 | 0.02480 | |
| 2 | 0.020 | 0.030 | 0.00276 | |
| 3 | 0.020 | 0.090 | 0.00828 | |
![]()
R =
k[ClO2][OH-]
R =
k[ClO2]2[OH-]
R =
k[ClO2][OH-]2
R =
k[ClO2]2[OH-]2
R =
[ClO2][OH-]-1
Questions 47 and 48 are based on the following information.
For a first order reaction the following
data are obtained from experiment
by
measuring the concentration as a function of time. The reaction is of the
type: A ® products.
| time (seconds) | 0 | 70 | 140 |
| [A] | 1.000 | 0.600 | ? |
![]()
0.500![]() 0.300
0.300![]() 0.360
0.360![]() 0.200
0.200![]() 0.000
0.000
7.30 x
10-3
140
0.693
0.600
70
Question 49 and 50 are based on the following.
- The rate constant, k, is measured at six different temperatures.
- The natural logarithm of k is plotted on the vertical axis (y-axis) and the reciprocal of the absolute temperature (1/T) is plotted on the horizontal axis (x-axis).
- The result is a linear plot with a slope equal to -6000 K and a y-intercept equal to 15.0
8.314![]() 6.00
6.00![]() 49.9
49.9![]() 15.0
15.0![]() 22.4
22.4
95![]() 70
70![]() 10
10![]() 287
287![]() 552
552