Questions 1 through 3 are based on the
following mechanism for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2) in the presence of the iodide ion
(I-).
- step 1..... H2O2
+I-® H2O +
OI-
step 2..... H2O2 + OI-®H2O + O2 + I-
2H2O2® 2H2O + O2
H2O2® H2 + O2
H2O2 + I- ® OI- + H2O
H2O2 + OI- ® H2O +
O2 + I-
H2O2 + I- ®2H +
2OI-
I-
H2O
OI-
O2
H2O2
I-
H2O
OI-
O2
H2O2
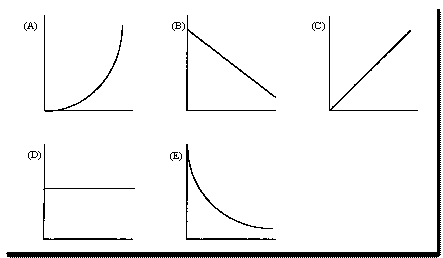
Questions 4 and 5 are based on the following
plots.
Select the letter of the plot
that best describes the relationships described below.
All questions pertain to reactions of the
type
A ® products. A plot may be used more than once in these questions.
A![]() B
B![]() C
C![]() D
D![]() E
E
A![]() B
B![]() C
C![]() D
D![]() E
E
332![]() 2880
2880![]() 5760
5760![]() 664
664![]() 1000
1000
Use the following information for questions 7 and 8.
The half life of a first order reaction of the type A ® products is 198s
![]()
49.5![]() 99.0
99.0![]() 396
396![]() 594
594![]() 792
792
1.01 x
10-2
2.50 x 10-2
3.50 x 10-3
5.00 x
10-3
7.00 x 10-3
| [C2H5Br] | [OH-] | Rate |
| 0.150 | 0.200 | 4.8 x 10-5 |
| 0.300 | 0.200 | 9.6 x 10-5 |
| 0.450 | 0.200 | 14.4 x 10-5 |
| 0.300 | 0.600 | 28.8 x 10-5 |
R =
k[C2H5Br]
R =
k[C2H5Br]2
R =
k[C2H5Br][OH-]
R =
k[C2H5Br]2[OH-]
R =
k[C2H5Br]2[OH-]3
It lowers
the activation energy for both the forward and reverse processes.
It
increases the rate of both the forward and reverse processes.
It may be recovered
unchanged at the end of the reaction.
It increases the
equilibrium constant.
It causes equilibrium to be reached more
rapidly.
logarithm
of specific rate constant versus the reciprocal of absolute temperature.
specific
rate constant versus absolute temperature.
specific rate
constant versus concentration of reactant.
rate of reaction
versus concentration of reactant.
logarithm of
concentration of reactant versus time.
0.0083
M![]() 0.32 M
0.32 M![]() 5.3 x
10-7 M
5.3 x
10-7 M![]() 0.014 M
0.014 M![]() 0.037
M
0.037
M
7.15![]() 14.3
14.3![]() 28.6
28.6![]() 25.0
25.0![]() 19.1
19.1
[A] |
[B] |
[C] |
Initial Rate
(M.s-1) | |
| 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.10 | 1.1 x 10-3 | |
| 0.050 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 4.4 x 10-3 | |
| 0.10 | 0.050 | 0.10 | 1.1 x 10-3 | |
| 0.10 | 0.050 | 0.30 | 3.3 x 10-3 | |
R =
k[A][B][C]
R = k[A]2[B]
R =
k[B][C]2
R = k[B]2[C]
R =
k[A][B][C]2
Use the following mechanism which has been proposed
for the reaction of
C4H9Br with OH- to answer
questions 15 through 17.
- Step 1........ C4H9Br
®C4H9+ +
Br- ........slow
Step 2........ C4H9+ + OH- ®C4H9OH........ fast
R =
k[C4H9Br][OH-]
R =
k[C4H9+][OH-]
R =
k[C4H9Br]
R =
k[C4H9Br][OH-][Br-]-1
R =
k[C4H9+]2
C4H9+
Br-
OH-
C4H9Br
There is
none.
C4H9+
Br-
OH-
C4H9Br
There is
none.
Question 18 is based on the following information.
The reaction between OCl- ions and
I- ions in NaOH solution is given by the following
equation:
OCl-(aq)
+ I-(aq) ®
OI-(aq) + Cl-(aq)
The following initial rates of the reaction were
measured at various
initial concentrations
as recorded in the table below.
Experiment |
[OCl-]0 |
[I-]0 |
[OH-]0 |
Initial Rate (M s-1) |
| 1 | 0.0040 | 0.0020 | 1.00 | 4.8 x 10-4 |
| 2 | 0.0020 | 0.0040 | 1.00 | 4.8 x 10-4 |
| 3 | 0.0020 | 0.0020 | 1.00 | 2.4 x 10-4 |
| 4 | 0.0020 | 0.0020 | 0.50 | 4.8 x 10-4 |
| 5 | 0.0020 | 0.0020 | 0.25 | 9.6 x 10-4 |
![]()
R =
k[OCl-][I-][OH-]2
R =
k[OCl-]2[I-][OH-]
R =
k[OCl-][I-][OH-]-1
R =
k[OCl-]2[I-]-1[OH-]
R =
k[OCl-][I-][OH-]
Questions 19 and 20 are based on the following information.
For a first order reaction the following data are obtained from an experiment by measuring the concentration as a function of time. The reaction is of the type: A ® products.
| time (secs.) | [A] |
| 0 | 1.00 |
| 50 | 0.500 |
| 100 | ? |
![]()
0.500![]() 0.250
0.250![]() 0.360
0.360![]() 0.200
0.200![]() 0.000
0.000
1.4x10-2
50
0.693
100
0.50
Questions 21 and 22 are based on the following:
The reduction of NO to N2 with H2; 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) = N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , is found to have the following experimentally determined rate equation: Rate = k[NO]2[H2]
![]()
0![]() 1
1![]() -1
-1![]() 2
2![]() -2
-2
Increase
two fold
Increase four fold
Decrease two
fold
Decrease four fold
Increase eight
fold
Questions 23 and 24 are based on the following
mechanism
for the conversion of ozone
to oxygen in the upper atmosphere.
- step 1. O3 + Cl ® O2 + OCl
step 2. O3 + OCl ® 2O2 + Cl
O3
+ Cl ®
O2 + OCl
O3 + OCl ® 2O2 + Cl
2O3® 3O2
3O2® 2O3
2O3 +Cl
+ OCl ®
3O2 + Cl + OCl
Cl
OCl
O3
O2
HCl