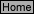R-6
E
ref
= E
ref
-
0.
0592
n
log Q
ref
Thus, Q = 1/1 and log Q reduces to zero, so that E
ref
= E°
ref
. The second step is to substitute the value
for E
ref
into equation (7) as E
red
if the reference half-cell is the cathode, or as E
ox
if the reference half-cell
is the anode. The value of E
cell
will be measured so E
test
can be calculated. The final step will be to
calculate the Q
test
using:
E
test
= E
test
-
0.
0592
n
log Q
test
From Q
test
, you can calculate the concentration of the metal ion in the test solution.
If using equation (8), E
cell
may be used directly with the concentration of the metal ion in the test half-
cell being the only unknown in the Q
cell
factor. The value of E
cell
is found using standard potentials for
each half-cell.
D. Solubility Product and Formation Constant
Solubility product constants, K
sp
, and formation constants, K
f
, are equilibrium constants for specific
kinds of reactions. The value of K
sp
is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of a solid in contact
with a saturated solution of its ions. The concepts of solubility product constants have been applied
extensively in the laboratory and are discussed in more detail in your textbook.
The formation constant, K
f
, is the equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from its
component metal ion and ligands. You have encountered complex ion formation in several previous
experiments. In this experiment, you will measure potential of a test cell containing a saturated solution
of a metal salt, and of a test cell containing a solution of a complex ion. You will calculate the respective
metal ion concentration in these cells, and then the values of K
sp
and of K
f
.
EXPERIMENTAL METHOD
Determination of Anode and Cathode